Chen: Entitry Relationship Model (1976)
Metadata
Title: The Entity-Relationship Model - Toward a Unified View of Data
Authors: Peter Pin-Shan Chen
Publication Year: 1976
Journal: ACM Transactions on Database Systems
Abstract
A data model, called the entity-relationship model, is proposed. This model incorporates some of the important semantic information about the real world. A special diagrammatic technique is introduced as a tool for database design. An example of database design and description using the model and the diagrammatic technique is given. Some implications for data integrity, information retrieval, and data manipulation are discussed.
The entity-relationship model can be used as a basis for unification of different views of data: the network model, the relational model, and the entity set model. Semantic ambiguities in these models are analyzed. Possible ways to derive their views of data from the entity-relationship model are presented.
Key Points
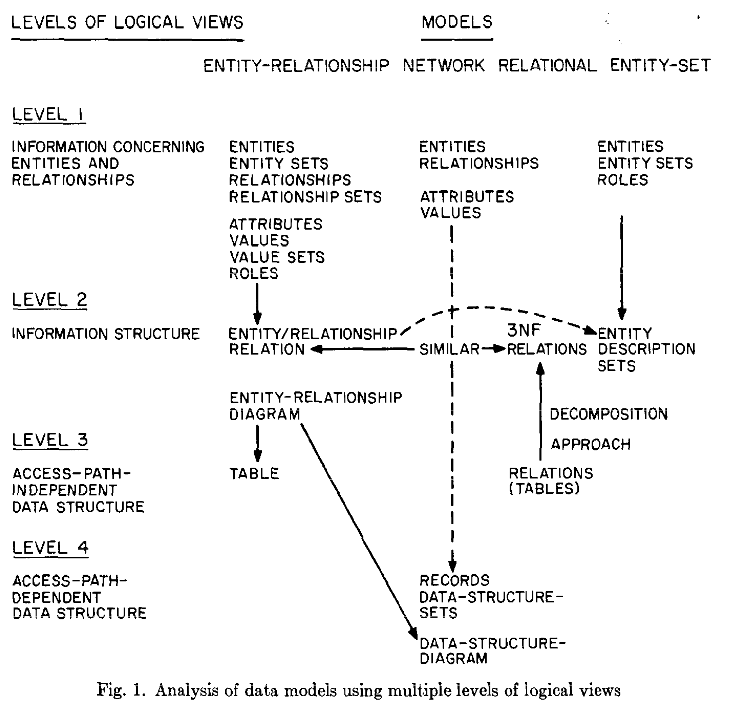
There are four levels of views of data:
Information concerning entities and relations that exist in our minds.
Information structure - organization of information in which entities and relationships are represented by data.
Access-path-independent data structures - structures that are not involved with query schemes, indexing schemes etc.
Access-path-dependent data structures.
Chen’s Entity-Relationship model focuses on the first two levels.
The relational model is concerned with levels 2 and 3.
The network (graph) model is concerned with level 4.
Relationships
A relationship set \(R_i\) is a mathematical relation among \(n\) entities, each taken from an entity set:
\[ \{ \left[ e_1, e_2, \dots , e_n \right] | e_1 \in E_1, e_2 \in E_2, \dots , \_n \in E_n \}\]
Each tuple of entities is a relationship.
The role of an entity in a relationship is the function that it peforms in the relationship. EG husband is the role played by an entity in the marriage relationship.
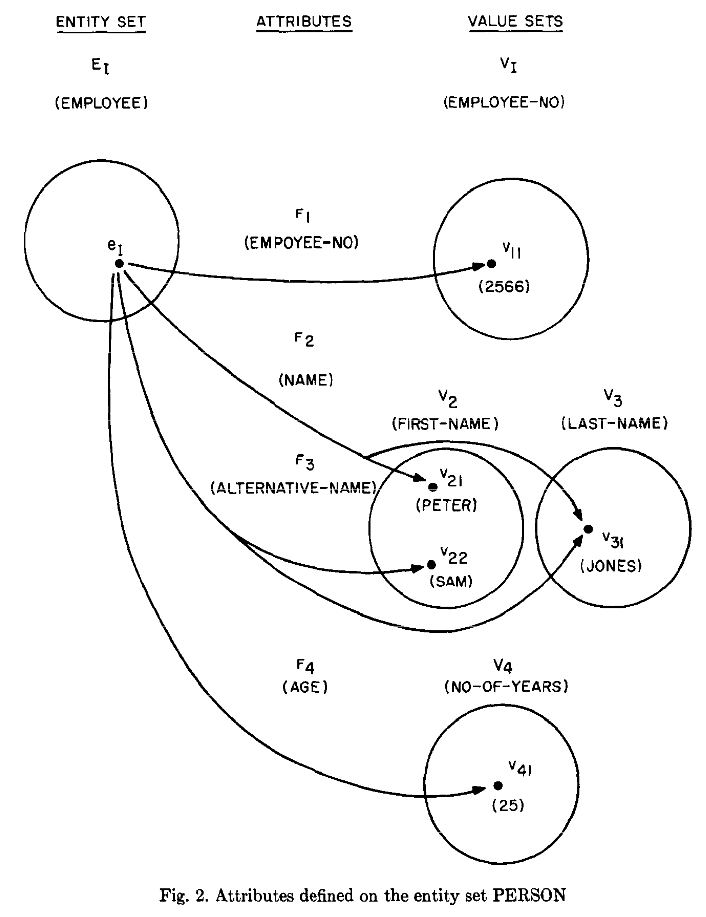
Attributes, Values, Value Sets
Information about an entity or relationship is expressed by a set of attribute-value pairs.
“2”, “red”, “Peter” are values.
Values are classified into different value sets like “Feet”, “Colour”, “First-Name”.
A predicate tests whether a value belongs to a value set.
An attribute is a function mapping an entity set or relationship set to a value set or Cartesian product of value sets.
\[f : E_i \mathrm{or} R_i \rightarrow V_i \mathrm{or} V_{i1} \times V_{i2} \times \dots \times V_{in}\]
Attributes are defined on an entity set. Eg attribute \(age\) maps from Person to value set NO-OF-YEARS. Or attribute \(name\) might map Person to the product of FIRST-NAME and LAST-NAME.
The rest of the paper walks through the diagram representation, comparisons with other data models (network and entity set), some coverage of data constraints.